GroupTheory`
GroupTheory`
GTCrystalField
GTCrystalField[group,lmax]
gives the crystal field Hamiltonian for a certain group up to a maximal angular momentum quantum number lmax.
Details and Options
- In the framework of perturbation theory, the influence of the crystal field can be expressed in terms of a crystal field potential
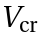 .
. - The crystal field potential can be expanded into spherical harmonics.
-
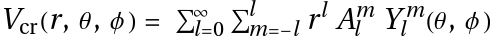
- The following options can be given:
-
GOFast False Controls the input validation GOHarmonics "Complex" Selects, which kind of spherical harmonics are used - See: W. Hergert, M. Geilhufe, Group Theory in Solid State Physics and Photonics. Problem Solving with Mathematica, chapter 7.4
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (1)
Options (3)
GOFast (2)
GOHarmonics (1)
Using GOHarmonics, it can be decided if the crystal field Hamiltonian is expanded into real or complex spherical harmonics.
Applications (2)
We consider the point group ![]() and calculate the crystal field Hamiltonian.
and calculate the crystal field Hamiltonian.
According to linear perturbation theory the matrix ![]() = (
= (![]() ,
,![]()
![]() ) is calculated. This can be simplified by using GTGauntCoefficient.
) is calculated. This can be simplified by using GTGauntCoefficient.
In the following the eigenvalues for an octahedral, a cubic and a tetrahedral crystal field are calculated and the parameters Dq[oct] and ϵ[oct] are introduced.