GroupTheory`
GroupTheory`
GTGroupQ
Details and Options
- A set
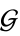 of elements
of elements 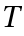 is called group if the four group axioms are satisfied:
is called group if the four group axioms are satisfied: - a) Closure: There exists an operation called multiplication which associates with every pair of elements
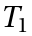 and
and 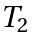 of
of 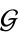 to another Element
to another Element 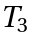 of
of 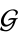 .
. - b) Associativity: For any three elements
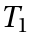 ,
, 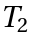 and
and 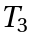 of
of 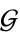 the "associative law" is valid.
the "associative law" is valid. - c) Identity element: There exists an Element
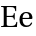 which is contained in
which is contained in 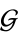 such that for every element
such that for every element 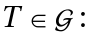
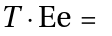
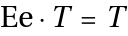 .
. - d) Inverse element: For each element
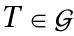 there exists an inverse Element
there exists an inverse Element 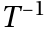 which is also contained in
which is also contained in 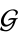 such that:
such that: 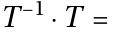
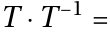
 .
. - The input can be of type symbol, matrix, quaternion or Euler angles (compare GTEulerAnglesQ, GTQuaternionQ and GTSymbolQ).
-
GOMethod "Numeric" Specifies the method to determine if a given list of elements is a group. - See: W. Hergert, M. Geilhufe, Group Theory in Solid State Physics and Photonics. Problem Solving with Mathematica, chapter 3.1.
Examples
open allclose allOptions (1)
GOMethod (1)
GTGroupQ calculates the multiplication table of a list of elements and determines if the resulting elements are members of the initial list. This evaluation can in general be performed numerically. For small groups the time difference between numerical and analytical evaluation is negligible. However, the difference becomes more prominent for large groups or highly dimensional group representations.
For double groups typical square root expressions slow down an analytic evaluation.