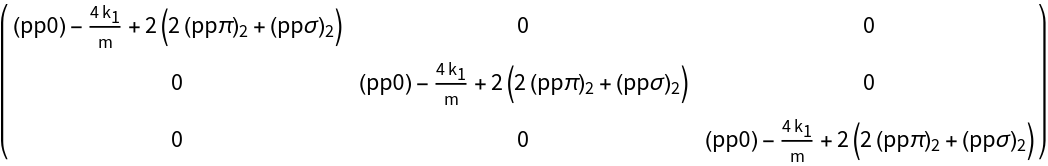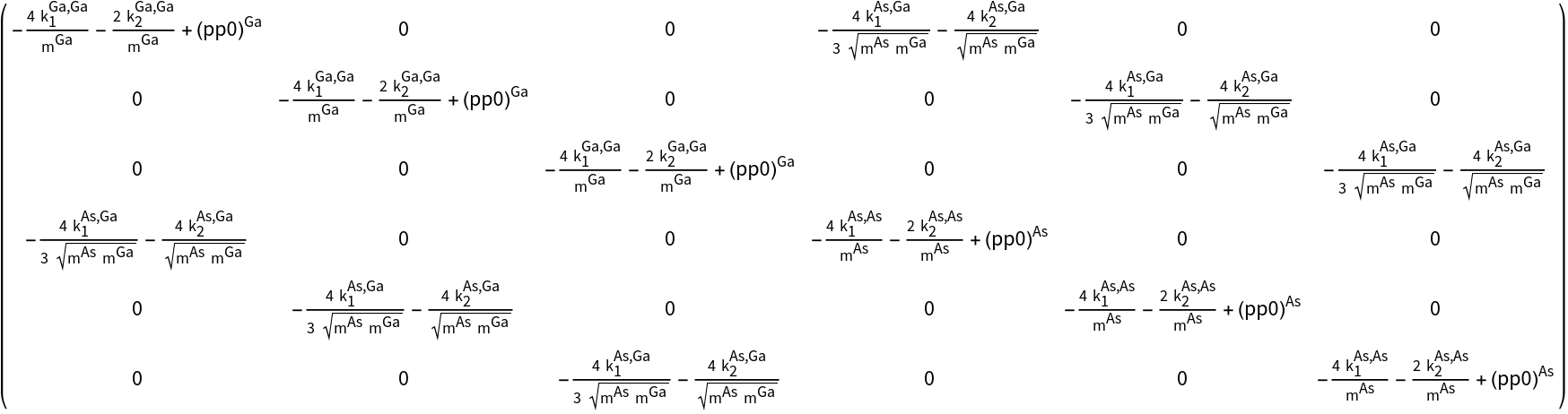GroupTheory`
GroupTheory`
GTVibTbToPhonon
GTVibTbToPhonon[p-Hamiltonian, shells]
transforms a tight-binding p-Hamiltonian in a dynamical matrix, taking into account shells.
Details and Options
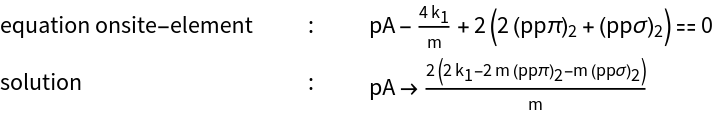
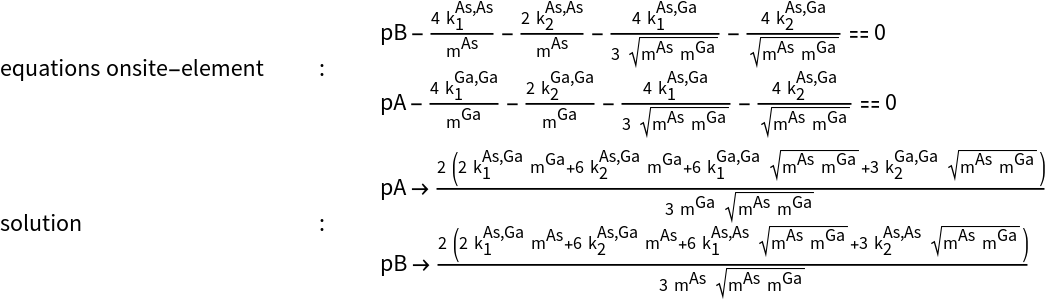
- The dynamical matrix to calculate phonon spectra for solids in a central force model can be generated starting from a tight-binding p-Hamiltonian.
- The hopping parameters (ppπ) have to be set to zero. The elements (ppσ) have to be substituted by the spring constants and the masses. The command performs this transformation.
- The on-site elements in the dynamical matrix are not independent like in the tight-binding Hamiltonian, but have to be calculated in dependence on the spring constants and masses.
- The following options can be given:
-
GOTbBasis 0 Supresses superscripts with element names GOVerbose True Controls the output of additional information - See: W. Hergert, M. Geilhufe, Group Theory in Solid State Physics and Photonics. Problem Solving with Mathematica, chapter 13.2.2
- See for the idea: R.M. Martin, Electronic Structure - Basic Theory and Practical Methods, Cambridge University Press 2004, p. 404