GTTbHamiltonian
GTTbHamiltonian[basis,lattice]
constructs the k-dependent Hamiltonian from the information about basis and lattice.
Details and Options
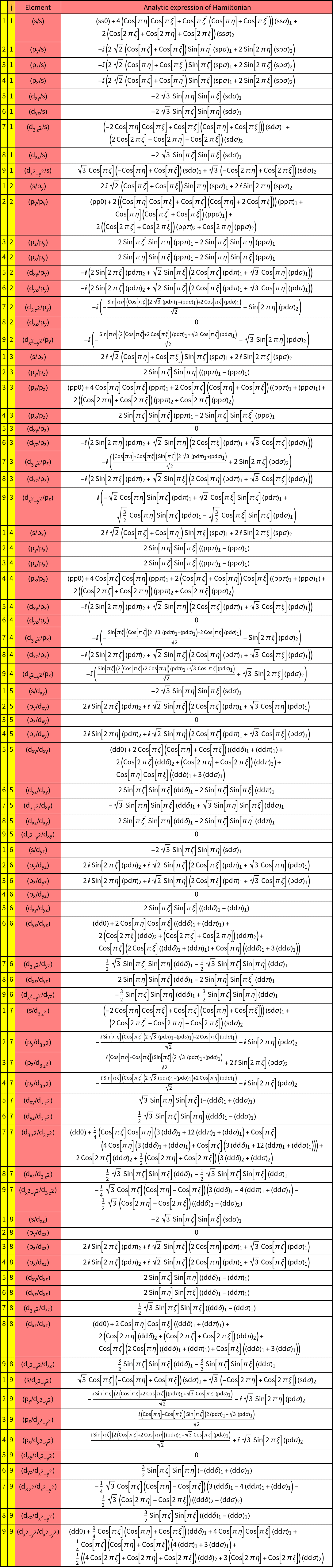
- The command constructs tight-binding Hamiltonians in two-center form from information about the atoms in the basis and the lattice. The Hamiltonian will be set up in a general form containing an appropriate notation of the hopping parameters and the general dependence on the wave vector k.
- The information about the basis contains the names of the corresponding elements and the angular momenta. The angular momenta are represented by a list. Therefore it is possible to adapt the Hamiltonian to a specific problem.
- It is possible to construct Hamiltonians for multiple atoms in the unit cell. If only one atom in the unit cell is present, the element name in the information about the basis is not used to construct the parameter names.
- If the structure is simple, the lattice information can be constructed by hand. Otherwise GTGetStructure allows to retrieve a structure from the space group database. The lattice information can be constructed from the space group information, GTCluster and GTShells.
- The lattice information is constructed as follows:
- lattice = {{interaction, number of shells, list of the positions in the shells},
{interaction, number of shells, list of the positions in the shells}, ... } - If only one atom is present, interaction=0 is used, otherwise interaction has to define the interaction between the different atoms in the basis. If we have two atoms "A", "B" in the basis, we have to define the interactions: "A,A", "B,B", "A,B"
- See: J. C. Slater, G. F. Koster,Simplified LCAO method for the periodic potential problem, Phys. Ref. 94, 1498-1524 (1954)
- W. Hergert, M. Geilhufe, Group Theory in Solid State Physics and Photonics. Problem Solving with Mathematica, chapter 9.4.1
Examples
Basic Examples (1)
If we want to construct the Hamiltonian for an fcc transition metal like Cu using s, p, d electrons in the basis we will set the basis information as:
For the fcc-structure the lattice information can be set up by hand, otherwise GTShells is used.
A better presentation of the matrix elements is given by means of GTHamiltonianList.
The NaCl structure contains two basis atoms. The information about the structure can be found in the space group database.
We construct a spherical cluster using this information:
The lattice constant is set to a = 1. Now the cluster is reordered in shells. Four shells around each basis atom are considered.
It can be seen that the Na atoms are surrounded by Cl atoms, and vice versa. We take into account only the Na-Cl interactions.
Because we want to study PbTe, we have to substitute the names of the atoms.
The information about the basis is, because only s and p electrons are considered: