GroupTheory`
GroupTheory`
GTTbHamiltonianElement
GTTbHamiltonianElement[l1,m1,l2,m2,shell,shell vectors]
constructs the k-dependent contribution of shell characterized by the shell vectors to the tight-binding matrix element between functions of symmetry ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Details and Options
- The tables in the seminal paper of Slater and Koster and a series of other papers in the field contain the k-dependent matrix elements of a tight-binding Hamiltonian including usually
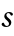 (
(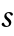 *),
*), 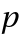 and
and 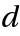 functions.
functions. - The tables are given for certain crystal structures. GTTbHamiltonianElement generates the analytical expressions automatically and therefore avoids mistakes. k-vectors are represented in units of 2π/a. The components of the k-vector are
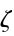 ,
, 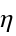 ,
, 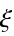 .
. - The following option can be given:
-
GOTbBasis 0 Supresses superscripts with element names - See: J. C. Slater, G. F. Koster,Simplified LCAO method for the periodic potential problem, Phys. Ref. 94, 1498-1524 (1954)
- W. Hergert, M. Geilhufe, Group Theory in Solid State Physics and Photonics. Problem Solving with Mathematica, chapter 9.4.
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (1)
We assume a cubic lattice. The vectors of the nearest neighbor shell are:
The Hamilton matrix element between to s function is given by
This is exactly the form given by Slater and Koster.![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() are the components of the k-vector in units 2π/a.
are the components of the k-vector in units 2π/a.
In some considerations of semiconductors an excited ![]() orbital
orbital ![]() * is included in the basis. This can be simulated using
* is included in the basis. This can be simulated using ![]() .
.