GroupTheory`
GroupTheory`
GTTbMatrixElement
GTTbMatrixElement[l1,m1,l2,m2,shell]
gives the decomposition of the tight-binding three-center integral between atom1 ![]() and atom2
and atom2 ![]() , when atom2 belongs to the neighborhood shell and atom2 is located in direction relative to atom1.
, when atom2 belongs to the neighborhood shell and atom2 is located in direction relative to atom1.
Details and Options
- In tight-binding theory the following integrals
-
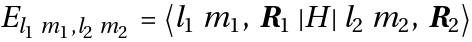
- have to be calculated. The Hamiltonian
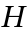 is represented in a Löwdin basis.
is represented in a Löwdin basis.  labels the atomic site and
labels the atomic site and  the angular symmetry with respect to this site. The energy integrals are expressed as a linear combination of two-center integrals in dependence on the direction cosines of the distance vector
the angular symmetry with respect to this site. The energy integrals are expressed as a linear combination of two-center integrals in dependence on the direction cosines of the distance vector  .
. - The following options can be given:
-
GOTbBasis 0 Supresses superscripts with element names GOTbRule 1 Selects substitution rules - See: A.V. Podolskiy, P. Vogl,Compact expression for the angular dependence of tight-binding Hamiltonian matrix elements, Phys. Rev. B 69, 233101 (2004)
- W. Hergert, M. Geilhufe, Group Theory in Solid State Physics and Photonics. Problem Solving with Mathematica, chapter 9.4
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (1)
The tight-binding matrix element will be expressed in terms of two-center-parameters and the direction cosines of the vector between the two atoms.
At the first atom a ![]() orbital is localized, at the second atom an
orbital is localized, at the second atom an ![]() orbital
orbital ![]() . The distance belongs to the nearest neighbor shell.
. The distance belongs to the nearest neighbor shell.
Usually ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() orbitals are used. The algorithm is general, also orbitals of higher angular momentum can be considered.
orbitals are used. The algorithm is general, also orbitals of higher angular momentum can be considered.
In some considerations of semiconductors an excited ![]() orbital
orbital ![]() * is included in the basis. This can be simulated using
* is included in the basis. This can be simulated using ![]() .
.