GroupTheory`
GroupTheory`
GTPhBandsObjects
GTPhBandsObjects[objects,background permittivity,reciprocal basis, cutoff, k-points, number of bands]
calculates number of bands of a photonic band structure at k-points. The system is defined by objects
and the given background permittivity. The reciprocal basis and cutoff are used to construct a cluster of reciprocal lattice vector.
Details and Options
- In GTPhMaster, GTPhMasterObjects and GTPhMasterPixel the eigenvalue problem of the master equation is constructed in a general form, the corresponding matrix can be stored as a function of
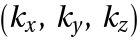 . The matrix can be used to calculate eigenvalues for bandstructures or densities of states. In the three-dimensional case the analytic expressions stored in the matrix becomes complex and the numerical evaluation for a large number of reciprocal lattice vectors becomes very time consuming. In GTPhBandsObjects the matrix is constructed for each k-point numerically. This speeds up three-dimensional considerably.
. The matrix can be used to calculate eigenvalues for bandstructures or densities of states. In the three-dimensional case the analytic expressions stored in the matrix becomes complex and the numerical evaluation for a large number of reciprocal lattice vectors becomes very time consuming. In GTPhBandsObjects the matrix is constructed for each k-point numerically. This speeds up three-dimensional considerably. - The list objects contains the description of the geometrical objects in the unit cell. The description of an objects is given by a list:
- objects = {{identifier, permittivity, geometry, shift},...}
- The identifier defines the name of the object. Furthermore the permittivity inside the object is defined. The list geometry defines filling factor, size and shape of the object. The object can be shifted with respect to the origin by the vector shift.
- The following option can be given:
-
GODCMethod "Direct" Method to calculate the matrix 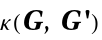
GODecimals 4 Controls the number of fractional digits in tables GOPhPol "Automatic" Specifies the polarization. GOPlotBands True Controls calculation of energy bands in the Brillouin zone. GOStore 0 Controls output of bands and eigenvalues to files. GOVerbose True Controls the output of additional information. - See: W. Hergert, M. Geilhufe, Group Theory in Solid State Physics and Photonics. Problem Solving with Mathematica, chapter 10
- K. M. Ho, C. T. Chan, C. M. Soukulis, Existence of a Photonic Gap in Periodic Dielectric structures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 3152 (1990).
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (1)
A circular rod in a quadratic unit cell is defined according to the rules in GTPhDCObjects.
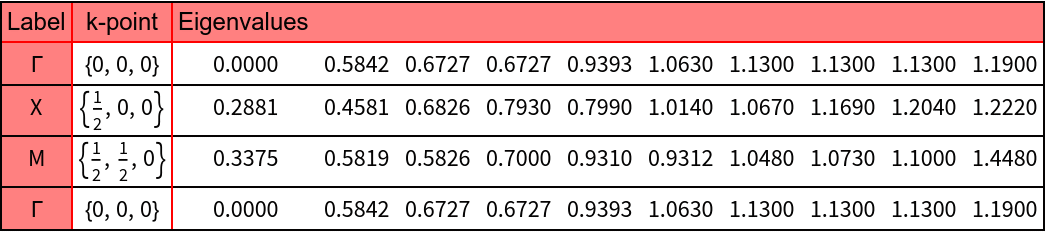
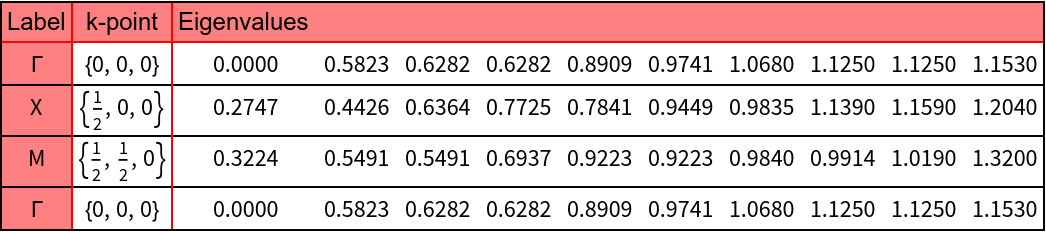
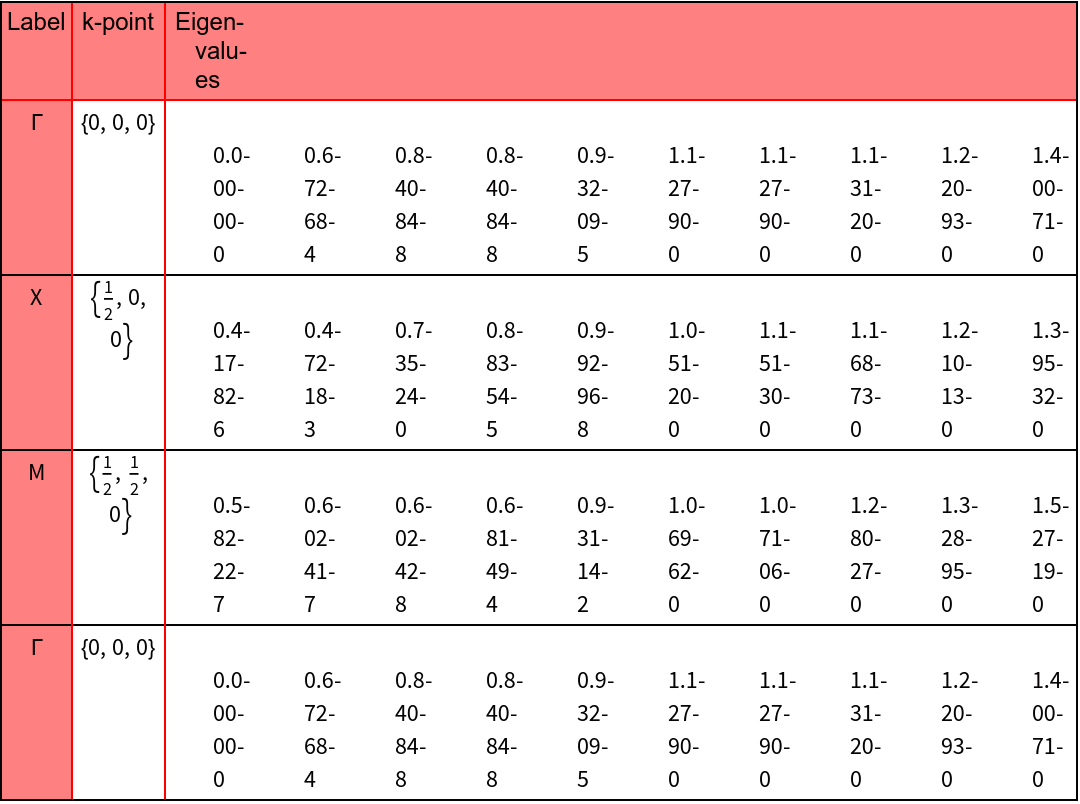
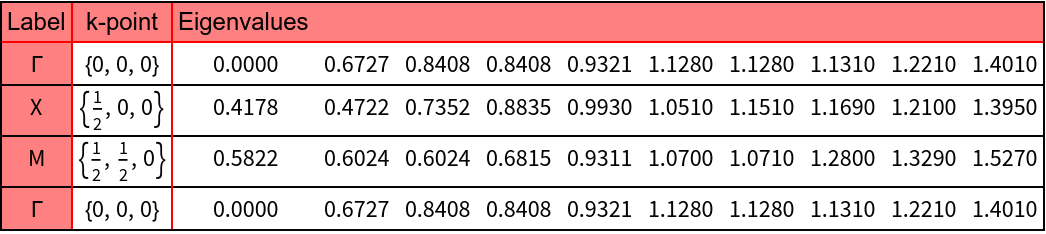
The path in the Brillouin zone for the plot of the photonic band structure is calculated.
The photonic bands for TE polarization are calculated and plotted.