mSASS part 2 - the d1 configuration in an octahedral field with spin-orbit coupling
The tutorial shows the construction of the mSASS-Hamiltonian for a d1 configuration in octahedral fields with spin-orbit interaction. It is a continuation of part 1 - d1 configuration in an octahedral field. More information can be found in the following reference:
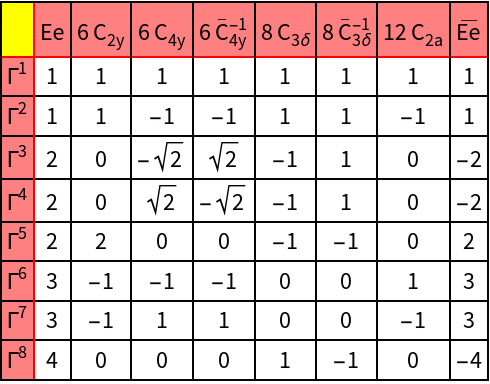
The octahedral symmetry is described by the point group O. Under spin-orbit coupling, a d-orbital splits into two orbitals with total angular momenta j=3/2 and j=5/2. First, we compute the character system of the SU(2) representations with j=3/2 and j=5/2 and analyze their decomposition into irreducible representations of O.
| GTInstallGroup | Installs point and space groups |
| GTCharacterTable | Comutes the character table |
| GTAngularMomentumChars |
Gives the characters of representations of O(3) or SU(2)
|
| GTIrep | Computes the decomposition of a reducible representation into irreducible representations of a group |
| GTAngularMomentumRep |
Computes representation matrices for the irreducible representations of O(3) or SU(2)
|
| GClebschGordanSum | Constructs the Clebsch-Gordan sum of two representations |
Construct super representation in terms of the Clebsch-Gordan sum of the j=3/2 and j=5/2 representation.