mSASS part 1 - d1 configuration in an octahedral field
| Expected level splitting | The mSASS Hamiltonian for the point group O |
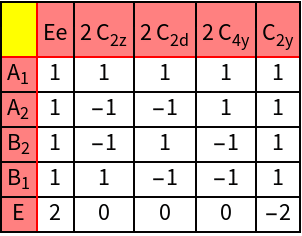
| Lowering the symmetry from octahedral to square symmetry | Lowering the symmetry to D4 |
The tutorial shows the construction of the mSASS-Hamiltonian for a d1 configuration in octahedral and square fields. More information can be found in the following reference:
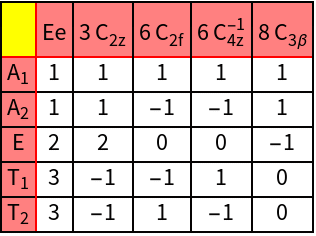
The octahedral symmetry is described by the point group O. First, we compute the character system of the SO(3) representation with l=2 and analyze its decomposition into irreducible representations of O.
| GTInstallGroup | Installs point and space groups |
| GTCharacterTable | Comutes the character table |
| GTAngularMomentumChars |
Gives the characters of representations of O(3) or SU(2)
|
| GTIrep | Computes the decomposition of a reducible representation into irreducible representations of a group |
| GTCrystalFieldSplitting | Compute the decomposition of representations upon lowering the symmetry |
| GTAngularMomentumRep |
Computes representation matrices for the irreducible representations of O(3) or SU(2)
|
The mSASS Hamiltonian is projected using the representation matrices of the angular momentum representation,
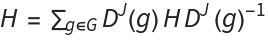 The right hand-side of the above equation is evaluated as follows.
The right hand-side of the above equation is evaluated as follows.
| GTGroupFromGenerators | Install a group from group generators |